Abnormal changes in the cartilage and bone of the spine that cause the development of the disease, according to the ICD-10 code, refer to the localization of M42 and are called thoracic osteonecrosis. The middle part of the spine is subjected to less stress than the lumbar and cervical spine, but deformities are difficult to heal. The load is unevenly distributed due to the rounded profile of the sternum, osteoblasts and other dysplastic manifestations appear.
Symptoms and signs
The disease occurs in the medullary nucleus of the disc, spreading to the capsule and other parts of the vertebral segment, where the mobility of the spine is guaranteed. The changes are manifested by compressive, reflexive or mixed neurological disorders and syndromes.
Pain manifests itself on exertion. There are different types of sensations:
- persistent mild pain in the chest area called low back pain;
- Severe and sharp abdominal pain, making it difficult to inhale or exhale, leading to immobility - back.
Symptoms and treatment of thoracic spondylosis depend on the degree of wear and tear of the skeletal apparatus and the stage of aging, both general and local.
Symptoms include:
- damage to the peripheral nerve processes (neuralgia), characterized by pain along the intercostal vasoconstrictors;
- pain focus on the left side of the chest or the appearance of strong painful sensations of a shingles nature;
- reduced mobility of the spine in the thoracic region;
- numbness in the arms and hands;
- decreased sexual function;
- the appearance of pain in the area of the internal organs, possibly for the heart, stomach, liver;
- low back pain in your neck, cheekbones, and head, cough, or a lump in your throat;
- arrhythmia, tachycardia, fever.
The signs of osteonecrosis are disguised as manifestations of related diseases, so the symptoms are vague. Spinal nerves are concentrated around the spine, when they are clamped, signals are sent to different parts of the body and organs.
Causes of osteonecrosis
There is no exact information about what factors deform the intervertebral discs. A common reason for osteonecrosis is scoliosis or curvature of the spine, which is more commonly noted in childhood and adolescence.
The theory considers such factors of vertebral deformity:
- heterogeneity;
- Hormonal;
- blood vessel;
- function;
- invisible;
- infection;
- immunity;
- metabolic disorder;
- mechanical;
- hereditary.
The deterioration and aging of bones and cartilage occurs due to prior exposure to adverse conditions. Spondylolisthesis is due to pre-determined genetic factors, the disease has clinical symptoms arising under the influence of exogenous and endogenous environment.
Consequences in the form of complications in the work of the vertebrae occur when the process of destruction of complex substances prevails in their synthesis. An exacerbation occurs when disk power is disordered and useful elements are missing. The entry of particles and degradation products is reduced, cell viability is reduced, and parts of the cell accumulate as a result of apoptosis. The production of complex proteins is reduced, collagen fibers are destroyed.
The mechanical impact on the annular bond formation increased, the layered structure was disorganized, the fibrous skeleton was torn. The disc is bruised under the influence of biomechanical and movement factors of the body, and its ability to fixation gradually decreases. Blood vessels and nerves can develop into rings due to a decrease in hydrostatic pressure.
Diagnostic method
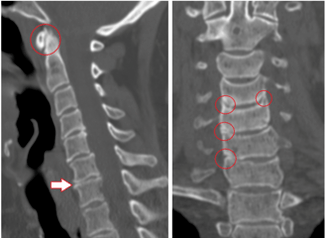
During recognition, lenticular, pain, reflex, muscle, autonomic, and vascular factors are identified. The best test method is difficult to determine, since in each case the diagnosis is made individually.
The main methods are:
- Diagnosis by X-ray;
- Computerized tomography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
X-ray analyzes the condition of the spine, images are given in the form of oblique, lateral and direct projection. Sometimes, for a photo, a person crouched down, not bent over or tilted to the side.
Contrast radiography is divided into the following studies:
- mechanical capture - 20 to 40 ml of air is injected into the spinal canal;
- angiography - 10 ml of contrast agent is injected into the vertebral lumen and 7 to 9 images are taken in 2 - 3 seconds;
- myelography - injection of a colored liquid is carried out into the subarachnoid lumen, followed by penetration of the structure;
- disc - a dye is injected directly into the disc for local examination.
Computed tomography evaluates bone and tissue structure, and the state of blood vessels. The painless method has three-dimensional images in minutes.
Benefits of CT:
- high detection speed;
- screening of "dumb" areas during diagnostics in motion;
- possibility of multipleural angiography;
- recognition of long objects with the acquisition of high-quality low-thickness cuts.
MRI uses the machine's magnetic field to generate hydrogen atoms in the human body in parallel with the activity. The particle signal, the response is recorded. The tomographer records the waves and displays the results on the screen. With MRI, without radiation, the method is less dangerous, but not recommended for pregnant women.
Treatment and prevention
Need to treat osteonecrosis in several stages, the level of complexity depends on the severity of the disease, contraindications and physical condition.
Method:
- drugs and therapeutic drugs;
- physical therapy methods, exercises to remove clamps, support the patient's condition;
- work.
There is a therapeutic movement, in which diseases of the spine such as hernia and spondylosis can be cured by rehabilitation exercise. In addition, a method of postoperative recovery has been developed.
Yoga exercises that help adult men, women, and children overcome pain, warn that the main thing is the psychological attitude.
Drugs
Medications prescribed by a neurosurgeon or neurologist consistent with the card and medical history. Patients taking medication in the hospital or at home, it is important to follow the instructions and not deviate from the oral regimen.
Common drugs:
- NSAIDs relieve pain, fever and inflammation;
- muscle relaxants that reduce the muscle tone of the skeleton;
- hormones that relieve neuropathic pain;
- vitamins B2, B6, B12, A and C are administered during simple remission and prophylaxis;
- diuretics reduce swelling and release pinched lens nerves;
- neurometabolic stimulant that improves metabolism in nervous tissues;
- chondroprotectors restore the cartilage of the vertebrae after damage.
Sometimes the patient does not take the drug at the beginning when the discomfort begins. Exercising, using a massager is enough.
Physical therapy

This type of exposure is used in combination with drug therapy or alone. In addition, lie down on the bed, apply heat to the painful area. Folk recipes are used to relieve pain.
Physical therapy in a medical facility includes procedures:
- ultrasound and electroacoustic;
- shock wave therapy;
- detensor effects;
- laser therapy;
- electrotherapy;
- magnetic field waves;
- mud therapy and sunbathing therapy;
- Massage.
Ultrasound involves the impact of high-frequency waves on tissues, reducing pain sensitivity. With super electrophoresis, analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are added for better delivery to the affected areas.
Shock wave therapy is the transmission of sound waves to the painful area, it is used to improve blood circulation, speed up metabolism. Detensor therapy involves stretching the spine using the patient's own body weight.
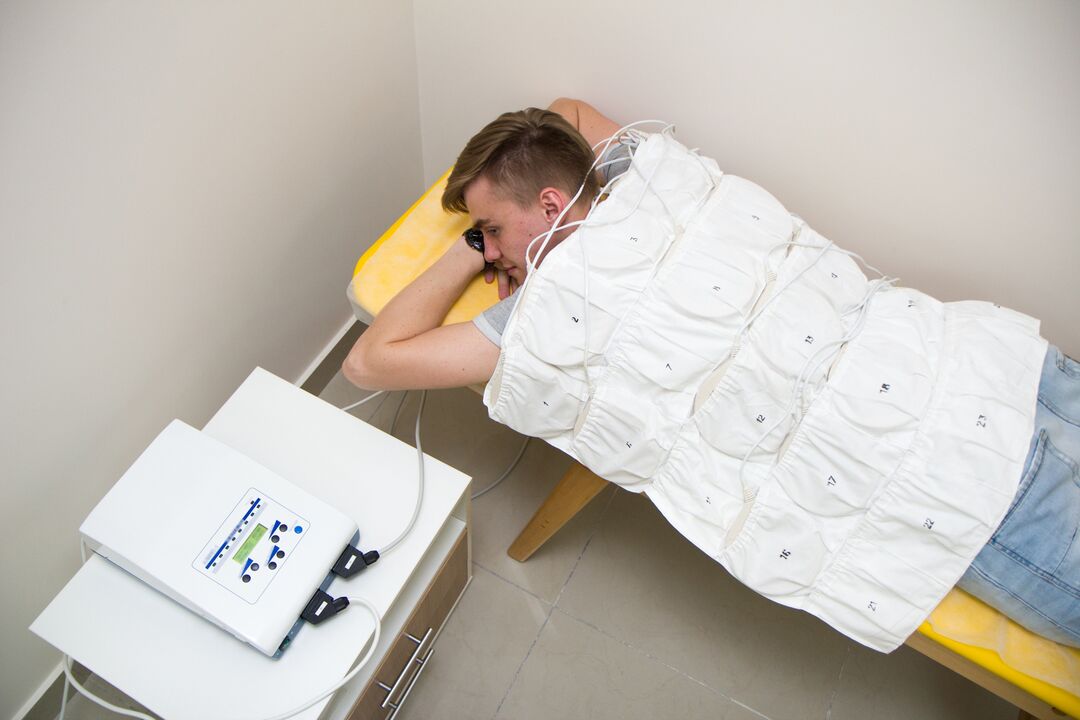

Laser therapy is based on helium-neon laser generation to activate bioelectrical currents in nerve fibers. The laser acts on the inflamed nerve roots in the disc area along the thoracic region.
Electrotherapy improves the nutrition and metabolism of products in the tissues, and the pulse currents affect the sensory nerve endings. Low-frequency waves relieve acute pain and are used as an initial measure of support.
Magnetic therapy is used to reduce swelling, spasms, and inflammation. A magnetic wave inductor is placed over the affected chest area. Balance therapy and mud therapy include swimming in pools, baths, and showers with contrast for treatment and recovery. Metabolism is normalized, blood flow to the affected areas is accelerated, pain and inflammation are reduced.
Therapeutic massage for thoracic spondylolisthesis is vacuum suction, point and lymphatic drainage, improve blood microcirculation, tissue nutrition and muscle firming. Lessons are conducted by a qualified professional, if you trust the spine for amateurs, dangerous consequences can occur. Massage is prescribed after the end of the acute phase, the first session not exceeding 10 minutes.
Surgical treatment
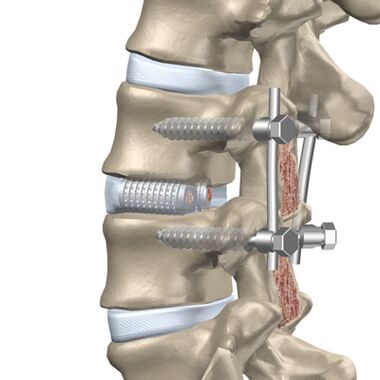
The patient is indicated for surgery if medical treatment, massage and other procedures do not reduce the patient's condition.
The intervention is divided into two phases:
- eliminate the cause of severe pain (decompensation);
- stability of the spine.
By the posterior approach, facet resection is performed, because facet joints can press on the nerve. Foraminotomy is the enlargement of the lens tube through which the nerve leaves the vertebrae. Spinal ablation removes the back part of the vertebrae, protects the spinal canal and compresses the brain due to deformity. Spondylectomy involves widening the opening of the spinal canal, where the spinal cord is located, while also removing a separate segment of the posterior region of the vertebrae.
Anterior surgery is performed if there is a condylar (bulging disc toward the lumen) or a herniated mass that protrudes toward the spinal canal.
The following methods are used for pre-decompression:
- discectomy - removal of the entire disc or a separate part of it;
- ablation - removal of the entire vertebra and adjacent discs followed by implantation.
Osteotomy and gastrectomy lead to column instability and an increased risk of neurological malformations. Rigid fixation or triple fusion (fusion) is used.
Prevention of osteonecrosis in the chest

Exacerbations of the disease reduce people's ability to work and quality of life, so prevention is particularly important. Therefore, cervical spondylosis occurs later and disability is avoided.
Methods of prevention:
- reduced physical activity on the spine;
- you cannot stand still for a long time without changing the supporting limb, you can lean on an improvised object or a wall;
- should not sit long at the desk and when working with the computer need to actively take breaks, move around a lot;
- selected mattress and orthopedic headrest for sleeping;
- while running and walking should avoid sudden jumps and jumps, wear damping shoes with small heels;
- Carrying objects weighing no more than 10 kg, gradually raise the body from the sitting position.
In a car, you need to use support bars for the back and headrests, and the driver's seat must be firm. Unable to do the work in a semi-reclined position, you can stand or sit. Well-developed muscles support the skeleton, so they pay attention to the workable and hard physical education.
Possible complications
The disease develops over a long period of time, sometimes painful symptoms do not come immediately. Any degenerative changes in the thoracic region lead to the appearance of pathologies.
Complications Types:
- pathology of the heart vessels with subsequent myocardial infarction or angina pectoris;
- intercostal neuralgia or peripheral neuritis with chest pain due to root compression;
- disc protrusion.
Complications occur with advanced forms of osteonecrosis, so prompt treatment in the early stages helps to avoid concomitant diseases.



























